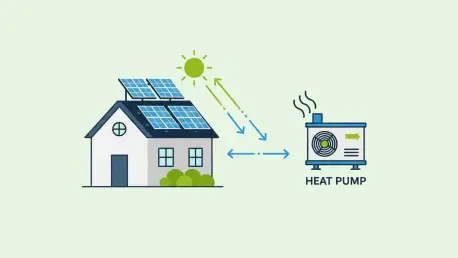
The relentless upward march of monthly utility bills has pushed many homeowners to seek not just efficiency but true energy independence from the power grid. The combination of solar panels and electric heat pumps represents a significant advancement in the residential energy efficiency sector. This review will explore the evolution of this synergistic technology, its key features, performance metrics, and the financial impact it has had on homeowners. The purpose of this review is to provide a thorough understanding of the system’s current capabilities and its potential for future development.
An Introduction to the Synergistic Technology
This pairing of technologies marries on-site power generation with high-efficiency consumption, creating a self-sustaining home energy loop. The core principle is straightforward: photovoltaic solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which in turn powers an electric heat pump to heat and cool the home. This integrated system has gained significant relevance amid the broader push for home electrification, offering a direct path away from fossil fuels.
The context for its emergence is one of growing economic and environmental urgency. Rising utility costs have made the operational expenses of traditional HVAC systems a significant financial burden for many. Consequently, homeowners are increasingly drawn to solutions that offer predictable energy costs and a smaller carbon footprint, making the solar-heat pump combination a timely and compelling upgrade.
Core Components and Performance Analysis
The Efficiency of Modern Heat Pumps
The electric heat pump stands as a cornerstone of this system, functioning with superior efficiency compared to traditional furnaces and air conditioners. Unlike systems that burn fuel to create heat, a heat pump moves existing heat from one place to another, a process that requires far less energy. This operational model allows it to achieve efficiency ratings several times higher than even the most advanced combustion-based heaters.
Modern advancements have also overcome a significant historical limitation: performance in cold climates. Today’s models maintain impressive reliability and output even in freezing temperatures, making them a viable option across diverse geographic regions. Their status as a high-demand electrical appliance makes them an ideal candidate for pairing with a home solar array, as their consumption can be directly offset by on-site generation.
The Role of Residential Solar Panels
The home solar panel system is the power plant of this integrated duo. These systems are designed to generate enough electricity to cover a significant portion, or even all, of a home’s energy needs. By harnessing solar energy, they effectively provide free fuel for the home’s electrical appliances after the initial installation cost is accounted for.
The primary function of the solar panels in this configuration is to eliminate the operational cost of the electric heat pump. When the sun is shining, the electricity produced can power the heat pump directly, drastically reducing reliance on the utility grid. This direct offsetting of a major energy consumer is what unlocks the most profound financial benefits of the combined system.
The Financial Synergy of the Combined System
When these two technologies are combined, they create a powerful financial synergy that exceeds the benefits of either component alone. The solar panels produce cost-free electricity, and the hyper-efficient heat pump uses that electricity to provide heating and cooling. This relationship leads to a dramatic reduction in monthly utility bills, a benefit supported by a growing body of real-world evidence.
This dual upgrade represents a compelling investment proposition for homeowners seeking to shield themselves from volatile and ever-increasing energy prices. By generating their own power to run their most demanding appliance, they gain a significant degree of control over their household expenses and achieve a new level of energy resilience.
Emerging Trends in Accessibility and Installation
Recent developments in the market have made this technology more accessible than ever before. Innovations in financing have lowered the barrier to entry, with some companies offering leasing programs and other arrangements that require no down payment. This shift allows homeowners to begin saving on their energy bills immediately, without a substantial upfront investment.
Furthermore, a robust ecosystem of companies and resources has emerged to guide homeowners through the adoption process. Firms like Mitsubishi and Palmetto offer specialized equipment and installation support, simplifying the transition. This growing infrastructure ensures that consumers have access to the expertise needed to design and implement a system tailored to their specific needs.
Real-World Application a Homeowner Case Study
The real-world application of this technology highlights its transformative potential. One notable case involved a homeowner who, after pairing a new heat pump with a solar array, saw their monthly electricity costs virtually disappear. This individual reported saving over $400 in a single winter month, effectively achieving complete energy independence from the local utility.
This example serves as a powerful demonstration of the system’s capabilities. It illustrates that the goal of eliminating an electric bill is not merely a theoretical possibility but an achievable reality for many. Such implementations underscore the system’s value as a practical and effective strategy for long-term financial savings and energy self-sufficiency.
Challenges and Market Adoption Hurdles
Despite its clear benefits, the technology faces several challenges that can hinder widespread adoption. The most significant hurdle is the initial upfront investment required for both a solar panel system and a new heat pump, which can be prohibitive for many households. Navigating local regulations, permitting processes, and utility interconnection agreements can also add complexity and delays to an installation.
To mitigate these limitations, federal tax credits and state-level incentive programs have been established to make the upgrade more affordable. These financial incentives can substantially reduce the net cost of the system, improving its return on investment. Continued efforts to streamline regulations and increase homeowner awareness are also critical to overcoming these market obstacles.
Future Outlook for Integrated Home Energy Systems
The trajectory for integrated home energy systems points toward greater efficiency, intelligence, and storage capabilities. Future developments will likely include more seamless integration with battery storage systems, allowing homeowners to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during power outages. This would create a truly resilient and self-sufficient home energy ecosystem.
As more homes move toward complete electrification—embracing electric vehicles, induction cooktops, and other appliances—the role of on-site generation and efficient consumption will become even more central. The solar-powered heat pump is a foundational element of this transition, paving the way for a future where homes operate as intelligent, self-sustaining energy hubs.
A Powerful Strategy for Modern Homeowners
The review of this synergistic technology made it clear that the combination of solar panels and electric heat pumps offered homeowners a powerful strategy to achieve energy independence. The system’s ability to drastically reduce or even eliminate electricity bills provided a financially sound solution to rising utility costs. The analysis of its components confirmed that modern heat pumps performed reliably in various climates while solar arrays supplied the necessary power at a minimal operational cost. Although initial investment remained a hurdle, emerging financing options and government incentives improved its accessibility. Ultimately, this integrated system stood as a cornerstone technology that empowered a fundamental shift toward residential energy self-sufficiency.