A speculative U.S. military intervention in Venezuela, hypothetically unfolding under a potential Trump administration, would fundamentally reshape the regional risk landscape by effectively neutralizing the nation’s long-standing territorial claim over Guyana’s resource-rich Essequibo region. Such a dramatic move, while drawing international condemnation, is analyzed as a decisive event that would primarily benefit neighboring Guyana and the powerful international energy corporations that have invested billions in its vast offshore oil fields. The central theme of this analysis is that direct American military action would not only depose the Maduro government but also incidentally resolve, through force, a century-old dispute that has been supercharged by the discovery of black gold, thereby securing massive U.S. economic interests in the burgeoning energy powerhouse. This action would create a new geopolitical reality, silencing a major source of regional instability and providing a powerful, albeit controversial, security guarantee for one of the world’s fastest-growing economies.
A Century-Old Conflict Reignited by Black Gold
The heart of the enduring conflict lies in the Essequibo territory, a sprawling, jungle-rich area that constitutes nearly two-thirds of Guyana’s landmass and is endowed with significant deposits of gold, diamonds, and, most critically, vast offshore crude oil reserves. The dispute’s origins trace back to an 1899 international arbitral tribunal that awarded the entire territory to Great Britain, which was Guyana’s colonial ruler at the time. Since gaining independence, Guyana has consistently upheld this ruling as final, legally binding, and the settled law of the land. In stark contrast, Venezuela has never accepted the legitimacy of the 1899 decision, persistently challenging Guyana’s sovereignty over the region through diplomatic protests, political pressure, and veiled threats. For over a century, this disagreement simmered, a point of national pride in Caracas and a source of constant, low-level anxiety in Georgetown, but it lacked the urgency to erupt into a full-blown crisis until the economic stakes were raised to an unprecedented level.
The modern dispute was dramatically reignited following a blockbuster oil discovery by U.S. energy giant Exxon Mobil in 2015, which unveiled enormous, high-quality crude oil reserves in the offshore waters administered by Guyana. This single event transformed the small nation of approximately 830,000 people into the world’s fastest-growing economy and an emerging major player in the global energy market. The newfound wealth attracted a torrent of foreign investment, particularly from American oil majors like Exxon Mobil and Chevron, as well as from China’s CNOOC. However, this economic miracle also intensified Venezuela’s territorial claims, prompting President Nicolas Maduro to adopt an increasingly aggressive posture. Maduro has repeatedly accused Guyana, the United States, and the involved oil firms of engaging in “legal colonialism” to rob Venezuela of its rightful territory. This escalating rhetoric culminated in late 2023, when Maduro’s government staged a referendum in which citizens purportedly approved claiming sovereignty over Essequibo, raising serious international concerns about a potential annexation attempt.
The Intervention Scenario and Its Immediate Impact
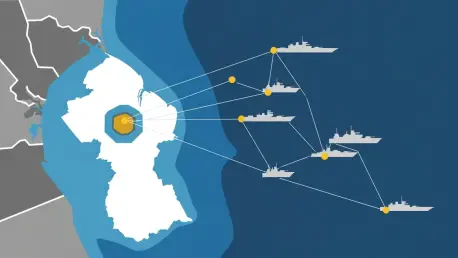
In a speculative scenario where a new Trump administration initiates a military intervention in Venezuela on January 3 to depose President Maduro, the action is depicted as sending immediate shockwaves across the globe. Such a move would predictably draw widespread condemnation as a flagrant breach of international law and national sovereignty. President Trump, in this hypothetical, is portrayed as dismissing these concerns, asserting that his actions are guided by his own moral compass rather than the constraints of international legal frameworks. According to analysts cited in the piece, the primary and most immediate consequence of this intervention would be the effective neutralization of Venezuela’s threat to Guyana’s territorial integrity. The sudden and overwhelming presence of a significant U.S. military force, described as an “armada” positioned off the Venezuelan coast, would serve as an insurmountable deterrent, prompting what is described as a “collective sigh of relief” from the energy majors operating in the region.
The practical security benefits of this military presence would be immense, mitigating the constant, underlying threat to critical infrastructure and personnel. Analyst Eileen Gavin of Verisk Maplecroft highlights this point, noting that a U.S. military presence would secure vulnerable logistics chains, vital shipping routes, and the highly expensive offshore oil facilities that form the backbone of Guyana’s economy. Within this scenario, President Trump is also portrayed as framing the military deployment as a necessary and justified measure to protect billions of dollars in American investments, effectively aligning U.S. foreign policy directly with its corporate economic interests. This shift would transform the regional security dynamic, replacing uncertainty and the threat of conflict with a firm, U.S.-enforced stability, allowing for the unhindered continuation of multi-billion dollar energy projects.
A New Regional Order and Future Considerations
Expert analysis largely converges on the conclusion that a U.S. intervention would effectively put Venezuela’s Essequibo claims “on ice” for the foreseeable future, fundamentally altering the regional power balance in favor of Guyana. The consensus among observers is that while President Maduro’s aggressive stance successfully created significant regional tension, its practical threat was always limited by the implicit potential for a U.S. response, given the heavy involvement of American corporations in Guyana’s oil sector. Allen Good, an equity research director at Morningstar, characterizes Maduro’s assertions as more “bluster” than a reflection of actionable military capability. He argues that any overt Venezuelan aggression against Guyana or Exxon Mobil would have likely provoked a U.S. response even without a full-scale intervention. With the U.S. now hypothetically in direct control of the situation in Caracas, the possibility of any Venezuelan action against its neighbor becomes “even more remote,” effectively “removing a nuisance” for both the Guyanese government and its corporate partners.
This hypothetical action would be a formalization of pre-existing U.S. commitments to Guyana’s security. In a speculative press conference held in March 2025, U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio is depicted alongside Guyanese President Irfaan Ali, where he warns Venezuela of severe consequences, including the potential use of military force, if it were to move against Guyana. This aligns with the broader theme that the United States has a vested strategic and economic interest in maintaining stability in Guyana to protect its assets. The intervention, therefore, would not be creating a new policy but rather enforcing an existing one in the most direct way possible. Following the hypothetical action, the bilateral security cooperation between the United States and Guyana would immediately strengthen, with Guyanese Foreign Secretary Robert Persaud noted as reaffirming Guyana’s commitment to its strategic alliance with the U.S. and welcoming American support in defending its sovereignty.
An Unsettled but Stabilized Future
The U.S. military action ultimately reshaped the regional power balance decisively in favor of Guyana and its international energy partners. By neutralizing the immediate military and political threat from Venezuela, the United States secured the operational environment for its energy companies and solidified its role as the primary security guarantor for Guyana’s vast and burgeoning oil wealth. While the underlying territorial dispute itself remained legally unresolved, its potential to destabilize the region and disrupt a multi-billion dollar industry was significantly diminished. The intervention had the effect of temporarily halting Venezuela’s territorial claims rather than eliminating them permanently, as the dispute is deeply ingrained in the Venezuelan national identity and would likely persist under a future regime with similar ideological leanings. However, with Caracas under intense pressure from the United States, it became highly improbable that it would prioritize making “much noise” about Essequibo. The crisis had been averted not through diplomacy, but through the overwhelming application of military and economic power, leaving a legacy of stability built on a foundation of unresolved historical grievances.